Imaging Workflow¶
This page describes the mzmine workflow for non targeted feature detection in imaging datasets. The workflow is designed for MS imaging data and tested with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation (MALDI)-MS data.
Tip
This workflow produces Feature lists as their result. Feature lists are a central part in visualizing the results in the Statistics dashboard and in the Interactive network visualizer.
Supported data formats¶
This workflow requires the spatial coordinates to be provided in the raw data file, which is the case in for the open-source imzML format. The native Bruker .d folders (with .tsf and .tdf data files) are also supported. Please note that ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) only supported in the native Bruker (tdf) format and not supported in imzML data.
Procedure overview¶
The general procedure is similar to the LC-MS workflow. The raw data is imported and noise is removed (raw data processing) prior to feature detection. Afterwards, multiple filters are available to refine the data.
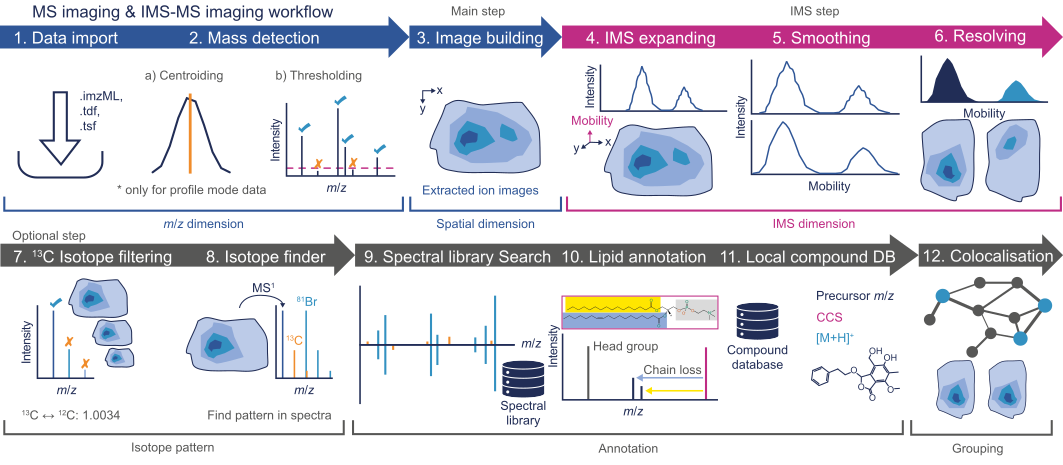
Raw data import and processing¶
Raw data is imported by a simple drag-and-drop gesture to the MS data files tab in the main window ( see Raw data import. After the data import, noise must be filtered from the raw data via the Mass detection module. Please note that this heavily impacts the performance of the whole workflow, since imaging spectra are usually richer in information than LC-MS spectra. If you experience performance (e.g., RAM issues), consider using a higher cutoff. IMS-MS imaging data sets require mass detection on the Frame and mobility scan level.
Feature detection¶
After mass detection, the feature detection is performed by the Image builder.
When working with IMS-MS imaging datasets, the ion mobility dimension should be added by the IMS expander after the image detection. After expanding, the IMS dimension must be resolved.
Isotope pattern and annotation¶
Isotope filtering, pattern finding, and feature annotation can be performed analog as described in the LC-MS workflow.
Warning
Tools, such as spectral library matching require MS2 spectra. Make sure yoour imaging data was acquired with MS/MS experiments.
Co-localization¶
Find co-located molecules using the Image co-localization module.
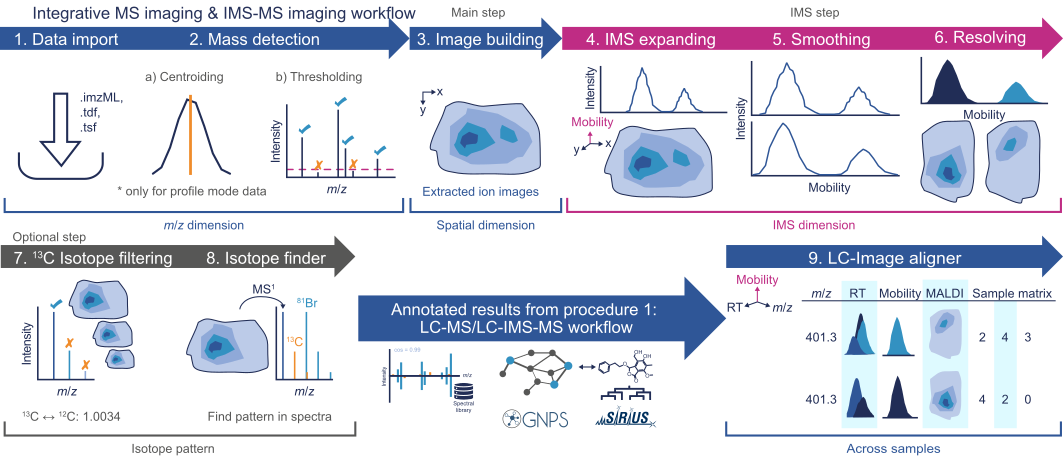
LC-Image aligner¶
If an LC-MS dataset was acquired for the imaging sample, the results can be aligned using the LC-Image Aligner. This allows integration of the two datasets and can be used for more confident identifications in imaging experiments. ( see https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-023-01690-2)
Feature filtering¶
After feature detection, the ion image features can be filtered to refine the results, for example by the Feature filter or the Rows filter. Additional filters are found in the Feature list methods → Feature filtering menu. When using the deisotoping modules, consider that there is no chromatographic separation.