Untargeted GC-MS Workflow¶
The workflow proposed herein is intended as a general pipeline for untargeted GC/EI-MS data preprocessing. GC/CI-MS can be processed analog to LC-MS. The main goal is essentially to turn the highly-complex GC-MS raw data into a list of features, and corresponding signal intensity, detected across the analysed samples. Such feature lists can then be annotated and/or exported for further downstream analysis (e.g., identification, search against spectral libraries, statistical analysis, etc.). A schematic representation of the workflow is shown below:
Tip
This workflow produces Feature lists as their result. Feature lists are a central part in visualizing the results in the Statistics dashboard and in the Interactive network visualizer.
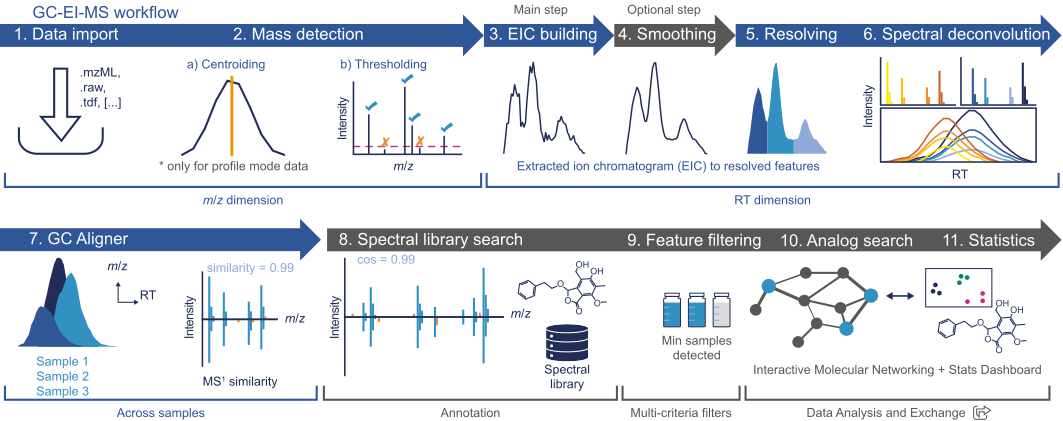
Raw data processing¶
The raw data processing consists of essentially two steps: Data import and Mass detection
Raw data import¶
Either open (e.g. mzML) and native vendor (e.g. Thermo, Bruker) data formats can be imported in mzmine. All the supported formats can be found here.
Mass detection¶
This step produces a list (referred to as "mass list") of the m/z values found in each MS scan across the LC run that exceed a user-defined threshold (i.e. noise level). For more details see the Mass detection module.
Feature detection¶
The goal of the "Feature detection" is to obtain a list of all the detected features (characterized by a RT and m/z value) from the raw GC-MS data.
Chromatogram building¶
The first step in the Feature detection is to build the extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) for each detected m/z (see Mass detection). For this, use the Chromatogram builder module.
The "detected" features in each file are listed in the so-called "feature lists", which are then further processed and aligned to connect corresponding features across all samples.
Smoothing in retention time dimension (optional)¶
Depending on the GC peak shape (i.e. data noisiness), the user can perform smoothing in retention time dimension. For more details see the Mass detection and Smoothing modules.
Feature resolving¶
Feature resolving step enables separation of co-eluting and overlapping chromatography peaks. It is one of the pivotal steps in data preprocessing. For more details on the algorithm used and parameters settings, see the Local minimum resolver module.
Spectral deconvolution¶
When using a hard ionization technique such as electron ionization (EI), multiple m/z values belong to the same compound. These m/z fragments can be grouped together based on their chromatographic behaviour (peak shape correlation). The grouping results in a cleaned up feature list as well as high quality deconvoluted GC/EI-MS spectra, perfect for spectral library matching. Find more info on spectral deconvolution here.
Feature alignment¶
Feature alignment enables alignment of corresponding features across multiple samples.
GC aligner¶
This module aligns detected features in different samples through a match score. The score is calculated based on the retention time and spectral similarity of each feature. For more information, see the GC aligner module.
Annotation, Filtering, Statistics and Export¶
Depending on the downstream analyses, there are several options which are accessible through the Feature list methods menu. Annotate compounds using spectral library search, apply various filtering criteria, explore the results using the statistics dashboard, or export the results.
Page Contributors¶