Spectral library search¶
Description¶
Feature list methods → Annotation → Search spectra → Spectral library search or with a right click on one or multiple selected feature rows Search → Spectral library search
The spectral library search module can be performed on feature lists, individual features (contained in feature list rows), or single scans.
Depending on the MS level (MS1 or MS2), all corresponding query scans (e.g., extracted from the rows) will be matched against selected spectral libraries that were previously imported.
Preferred ways to import libraries are in this order:
-
together with spectral data files in the advanced data import:
Raw data methods → Raw data import → MS data (advanced)
-
drag and drop into the main window
-
with a dedicated import module:
Raw data methods → Raw data import → Spectral library import or from Feature list methods → Annotation → Search spectra → Import spectral libraries.
Downloads for open spectral libraries¶
- MassBank of North America: download (download .json)
- MassBankEU: download (download *_NIST.msp)
- GNPS (ALL_GNPS_NO_PROPOGATED): download (download .json)
- MSnLib: download (download .mgf)
- GC/EI-HRMS for lipids: download (download .json)
Supported library formats¶
- *.json: MassBank of North America (MoNA)
- *.json: The Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) (format from the spectral DB submission module)
- *.mgf: GNPS
- *.msp: MoNA, MassBankEU (NIST compatible), National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- *.jdx: JCAMP-DX
Parameters¶
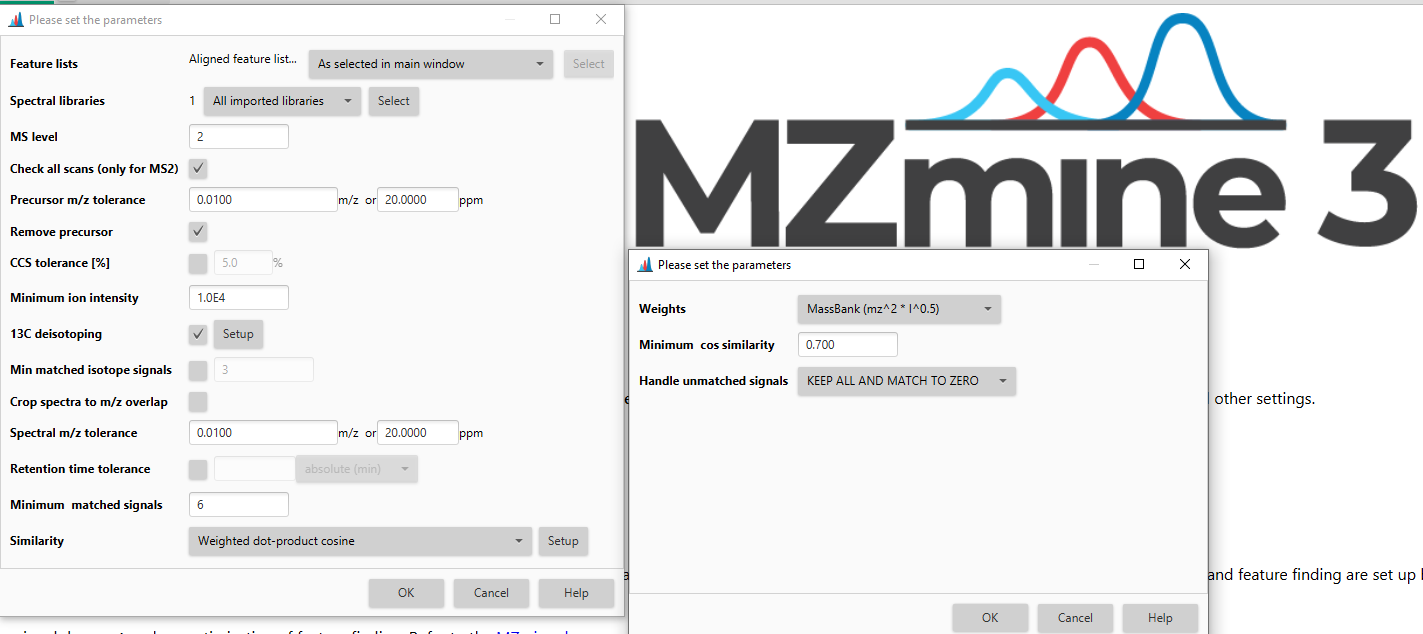
Spectral libraries¶
The spectral libraries of interest need to be imported before applying spectral library search. Either uses all imported spectral libraries or only the selected libraries.
Merge & select fragment scans¶
This parameter controls how fragment spectra are filtered, merged, and selected for downstream analysis (see detailed description). Briefly, either choose preset based spectral merging, input scans without merging, or an advanced setup for more options.
For spectral library matching mzmine recommends using the representative scans = one for each fragmentation energy and one merged across all.
MS level filter¶
Select MS2 for fragment spectra with precursor m/z.
Select MS1 for GC-EI-MS spectra.

Precursor m/z tolerance¶
This option is only used for MS level > 1. Here, the library entries are filtered by their precursor m/z reducing the number of spectral-pairs to match.
The absolute (in m/z) and relative (in ppm) m/z tolerance can be set. The maximum tolerance for each precursor is applied.
Considering that the precursor isolation window is often far greater than the resolution or accuracy of the MS scan, this parameter is often set to higher m/z tolerances.
Another aspect is the used library, which might contain uncalibrated reference spectra from lower resolution instruments.
Spectral m/z tolerance¶
This m/z tolerance is used to pair signals in the query and library scans. It can be set in absolute (in m/z) and relative (in ppm) m/z tolerance, whereas the maximum tolerance for each m/z value is applied. It must be kept in mind, which mass resolutions are achieved within the experimental spectra and within the spectral library.
Remove precursor¶

Depending on the fragmentation method, e.g., collision induced dissociation (CID) or higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD), the precursor can be detected with different intensities resulting in varying cosine similarities during the library matching.
Therefore, this option enables the removal of the precursor signal (± 4 Da) prior to the matching.
Min matched signals¶
The query mass list and spectral library entry must contain at least this number of matched (paired) m/z values (+- m/z tolerance).
Common parameters include 4 signals for smaller molecules and 6 for more confident matches.


Similarity¶
Several algorithms can be applied to calculate the similarity of the query and library scans and to filter the resulting library matches. The available algorithms are:
- Weighted cosine similarity,
- Composite cosine identity (e.g., GC-EI-MS; similar to NIST search).
More details are available here.
The weighted cosine similarity is used for comparing MS2 data, whereas the composite cosine identity (e.g., GC-EI-MS; similar to NIST search) considers the relative intensity of neighboring signals and is, therefore, applied to MS1 spectra from GC-EI-MS.
Retention time tolerance¶
These option can be used to include these values as further spectral matching identifiers. The maximum allowed retention time difference when comparing the query and library scan. It can be set in absolute (min or sec) or relative (%) values.
This option is intended for in-house libraries or standardized libraries that follow the same acquisition protocol with the same set-up, e.g., column, instrument, and method).

CCS tolerance¶
The collision cross-section (CCS) tolerance can be used in a similar way as the retention time tolerance.
Accordingly, the CCS value of a query will be compared with the library entries and the maximum tolerance can be set in %.

Retention index tolerance¶
This option can be used to exclude library entries that are not sufficiently close in retention index.
Skip library entries without RIs¶
This option can be used to exclude library entries that do not have a defined retention index for the selected column type. Otherwise, those library entries can be used to match any row.
13C deisotoping¶
This option allows to remove potential 13C isotope signals in the experimental spectrum before the library search. It can be enabled when co-isolation of precursor’s 13C isotopes is expected during MS2 data acquisition (e.g., isolation window > 1 Da). Following parameters can be set:
-
m/z tolerance: Maximum allowed difference between the measured and predicted isotope m/z values. The absolute (in m/z) and relative (in ppm) m/z tolerance can be set, whereas the maximum tolerance for each m/z value is applied.
-
Monotonic shape: If enabled, the monotonically decreasing height of isotope pattern is required.
-
Maximum charge: The maximum charge that will be considered for detecting the isotope pattern. For singly charged ions, the 13C isotope will be expected +1 whereas for doubly charged ions it will be +0.5 (+1 m/z divided by the charge 2).
Min matched isotope signals¶
This option can be used to set a minimum number of matched 13 isotopes signals. It is only useful if the query AND library entries contain isotope patterns (e.g., in MS1 or with wider precursor isolation windows).
The minimum number of matched signals of 13C isotopes.

Crop spectra to m/z overlap¶
This option can be used to consider only the mass range where both the experimental and library spectra exhibit m/z signals. All other signals are ignored during the matching. For example, if query and library scans were acquired with different methods, e.g., mass range, fragmentation energy or mode, it can be helpful to crop the spectra to their overlapping m/z range (+ m/z tolerance). This is done by using the maximum m/z range where both spectra contain signals. However, this tends to return more false positive matches. Therefore, we recommend extra curation of the matching results when this option is enabled.