Savitzky-Golay resolver¶
Description¶
Feature detection → Chromatogram resolving → Savitzky Golay resolver
This method uses the Savitzky-Golay polynomial [1] to calculate the smoothed second-derivative of the chromatogram's intensities.
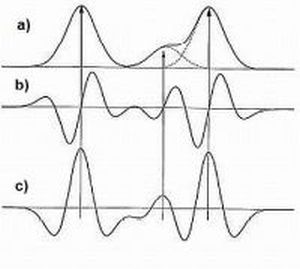
The following figure (left) presents the shape of a) a Gaussian peak, b) the first derivative, and c) the second derivative.
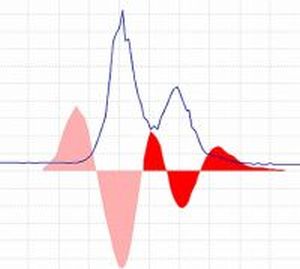
The figure on the right side shows how the signal (blue line) may be divided into individual chromatographic peaks by observing the second derivative.
References¶
- A. Savitzky and M. J. E. Golay, Anal. Chem., 36, 1627 (1964). DOI: 10.1021/ac60214a047
Parameters¶
Suffix
This string is added to feature list name as suffix
Original feature list
Defines the processing. Standard is to KEEP the original feature list and create a new processed list.
REMOVE saves memory.
PROCESS IN PLACE is an advanced option to process directly in the feature list and reduce memory consumption more - this might come with side effects, apply with caution.
MS/MS scan pairing
Set MS/MS scan pairing parameters. For more details see MS2 scan pairing
Min peak height
Minimum acceptable feature height (absolute intensity)
Peak duration range
Range of acceptable feature durations
Derivative threshold level
Minimum acceptable intensity in the second derivative for feature recognition
Min # of data points
Minimum number of data points on a feature.